All you need to know before going for a REACT.JS interview
BASIC
STUFF :-
There are a couple primary pillars in the JavaScript toolchain:
Dependency Management, Linting, Style-checking, Transpilation, and Compilation,
Minification, Source-Mapping.
PROPS and
STATE :-
Props is the shorthand for Properties in React. They are read-only
components which must be kept pure i.e. immutable. They are always passed down
from the parent to the child components throughout the application. A child
component can never send a prop back to the parent component. This help in
maintaining the unidirectional data flow and are generally used to render the
dynamically generated data.
States are the heart of React components. States are the source of
data and must be kept as simple as possible. Basically, states are the objects
which determine components rendering and behavior. They are mutable unlike the
props and create dynamic and interactive components. They are accessed via
this.state().
Every component's props object has a property named children.
this.props.children will return everything in between a
component's opening and closing JSX tags.
There are two ways for a component to get dynamic information:
props and state. Besides props and state, everything in a component should
always stay exactly the same.
A component changes its state by calling the function
this.setState
Any time that you call this.setState, this.setState AUTOMATICALLY
calls render as soon as the state has changed.
Think of this.setState as actually being two things:
this.setState, immediately followed by render.
That is why you can't call this.setState from inside of the render
function!this.setState automatically calls render. If render calls
this.setState, you will create an infinite loop
a stateful component passes
its state down to a stateless component.
A React component should use props to store information that can
be changed, but can only be changed by a different component.
A React component should use state to store information that the
component itself can change.
Stateless functional components usually have props passed to them
:-
(JS function without render function )
propTypes are useful for two reasons.
1) The first reason is prop validation.
2) 2 is arguably more useful: documentation.
If you add .isRequired to a propType, then you will get a console
warning if that prop isn't sent.
A controlled component, on the other hand, has no memory. If you
ask it for information about itself, then it will have to get that information
through props. Most React components are controlled.
In React, when you give an <input /> a value attribute, then
something strange happens: the <input /> BECOMES controlled
Lifecycle methods are methods that get called at certain moments
in a component's life.
You can write a lifecycle method that gets called right before a
component renders for the first time.
You can write a lifecycle method that gets called right after a
component renders, every time except for the first time.
You can attach lifecycle methods to a lot of different moments in
a component's life. This has powerful implications!
There are three categories of lifecycle methods: mounting,
updating, and unmounting.
A component "mounts" when it renders for the first time.
This is when mounting lifecycle methods get called.
/* start of life cycle */
There are three mounting lifecycle methods:
componentWillMount
When a component renders for the first time, componentWillMount
gets called right before render.
setTimeout(function(){
ReactDOM.render(
<Example />,
document.getElementById('app')
);
}, 2000);
componentWillMount does NOT get called, because mounting lifecycle
events only execute the first time that a component renders.
render
render is a lifecycle method!
render belongs to two categories: mounting lifecycle methods, and
updating lifecycle methods.
componentDidMount
When a component mounts, it automatically calls these three
methods, in order.
There are five updating lifecycle methods:
componentWillReceiveProps
When a component instance updates, componentWillReceiveProps gets
called before the rendering begins.
shouldComponentUpdate
If shouldComponentUpdate returns true, then nothing noticeable
happens. But if shouldComponentUpdate returns false, then the component will
not update! None of the remaining lifecycle methods for that updating period
will be called, including render.
componentWillUpdate
componentWillUpdate gets called in between shouldComponentUpdate and
render.
The main purpose of componentWillUpdate is to interact with things
outside of the React architecture.
If you need to do non-React setup before a component renders, such
as checking the window size or interacting with an API, then
componentWillUpdate is a good place to do that
render
componentDidUpdateWhen a component instance updates,
componentDidUpdate gets called after any rendered HTML has finished loading.
Whenever a component instance updates, it automatically calls all
five of these
unmounting:-
componentWillUnmount
Here you can cancel any outgoing network requests, or remove all
event listeners associated with the component.Basically, clean up anything to
do that solely involves the component in question — when it’s gone, it should
be completely gone.
Lifecycle pic :-
https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/lifecycle_reactjs.jpg
/* End of lifecycle */
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
General
Interview questions
1. a) How React works? How Virtual-DOM works in React?
React creates a
virtual DOM. When state changes in a component it firstly runs a “diffing”
algorithm, which identifies what has changed in the virtual DOM. The second
step is reconciliation, where it updates the DOM with the results of diff.
The HTML DOM is always tree-structured — which is allowed by the
structure of HTML document. The DOM trees are huge nowadays because of large
apps. Since we are more and more pushed towards dynamic web apps (Single Page
Applications — SPAs), we need to modify the DOM tree incessantly and a lot. And
this is a real performance and development pain.
The Virtual DOM is an abstraction of the HTML DOM. It is lightweight
and detached from the browser-specific implementation details. It is not
invented by React but it uses it and provides it for free.
ReactElements lives
in the virtual DOM. They make the basic nodes here. Once we defined the
elements, ReactElements can
be render into the "real" DOM.
Whenever a
ReactComponent is
changing the state, diff algorithm in React runs and identifies what has
changed. And then it updates the DOM with the results of diff. The point is -
it’s done faster than it would be in the regular DOM.b) Differentiate between Real DOM and Virtual DOM.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| render(){ return( <div> <h1> Hello World from Edureka!!</h1> </div> );} |
7) How is React different from Angular?
TOPIC REACT ANGULAR 1. ARCHITECTURE Only the View of MVC Complete MVC 2. RENDERING Server-side rendering Client-side rendering 3. DOM Uses virtual DOM Uses real DOM 4. DATA BINDING One-way data binding Two-way data binding 5. DEBUGGING Compile time debugging Runtime debugging 6. AUTHOR Facebook Google
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| //General wayrender() { return( <MyInput onChange={this.handleChange.bind(this) } /> );}//With Arrow Functionrender() { return( <MyInput onChange={ (e) => this.handleOnChange(e) } /> );} |
Following are the cases when refs should be used:
- When you need to manage focus, select text or media playback
- To trigger imperative animations
- Integrate with third-party DOM libraries
10) How do you modularize code in React?
We can modularize code by using the export and import properties. They help in writing the components separately in different files.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| //ChildComponent.jsxexport default class ChildComponent extends React.Component { render() { return( <div> <h1>This is a child component</h1> </div> ); }}//ParentComponent.jsximport ChildComponent from './childcomponent.js';class ParentComponent extends React.Component { render() { return( <div> <App /> </div> ); }} |
Higher Order Component is an advanced way of reusing the component logic.
HOC are ‘pure’ components.
HOC can be used for many tasks like:
- Code reuse, logic and bootstrap abstraction
- Render High jacking
- State abstraction and manipulation
- Props manipulation
Keys are used for identifying unique Virtual DOM Elements with their corresponding data driving the UI. They help React to optimize the rendering by recycling all the existing elements in the DOM. These keys must be a unique number or string, using which React just reorders the elements instead of re-rendering them. This leads to increase in application’s performance.
React Redux – React Interview Questions13) What were the major problems with MVC framework?
Following are some of the major problems with MVC framework:
- DOM manipulation was very expensive
- Applications were slow and inefficient
- There was huge memory wastage
- Because of circular dependencies, a complicated model was created around models and views
Flux is an architectural pattern which enforces the uni-directional data flow. It controls derived data and enables communication between multiple components using a central Store which has authority for all data. Any update in data throughout the application must occur here only. Flux provides stability to the application and reduces run-time errors.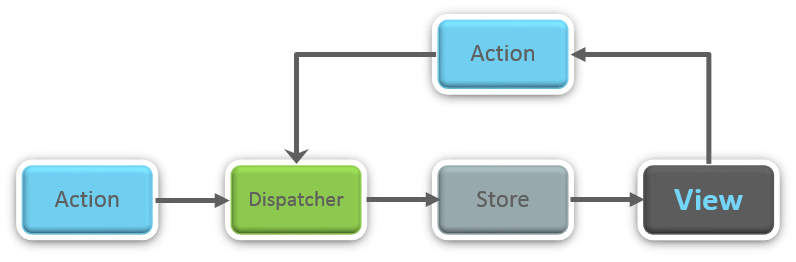

15) What is Redux?
Redux is one of the hottest libraries for front-end development in today’s marketplace. It is a predictable state container for JavaScript applications and is used for the entire applications state management. Applications developed with Redux are easy to test and can run in different environments showing consistent behavior.
16) What are the three principles that Redux follows?
- Single source of truth: The state of the entire application is stored in an object/ state tree within a single store. The single state tree makes it easier to keep track of changes over time and debug or inspect the application.
- State is read-only: The only way to change the state is to trigger an action. An action is a plain JS object describing the change. Just like state is the minimal representation of data, the action is the minimal representation of the change to that data.
- Changes are made with pure functions: In order to specify how the state tree is transformed by actions, you need pure functions. Pure functions are those whose return value depends solely on the values of their arguments.
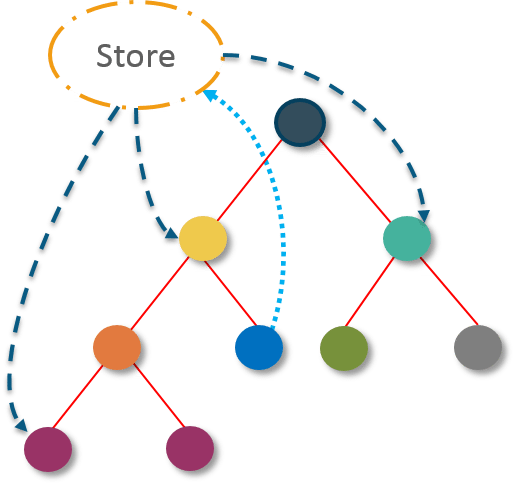
17) What do you understand by “Single source of truth”?
Redux uses ‘Store’ for storing the application’s entire state at one place. So all the component’s state are stored in the Store and they receive updates from the Store itself. The single state tree makes it easier to keep track of changes over time and debug or inspect the application.
18) List down the components of Redux.
Redux is composed of the following components:
- Action – It’s an object that describes what happened.
- Reducer – It is a place to determine how the state will change.
- Store – State/ Object tree of the entire application is saved in the Store.
- View – Simply displays the data provided by the Store.
19) Show how the data flows through Redux?
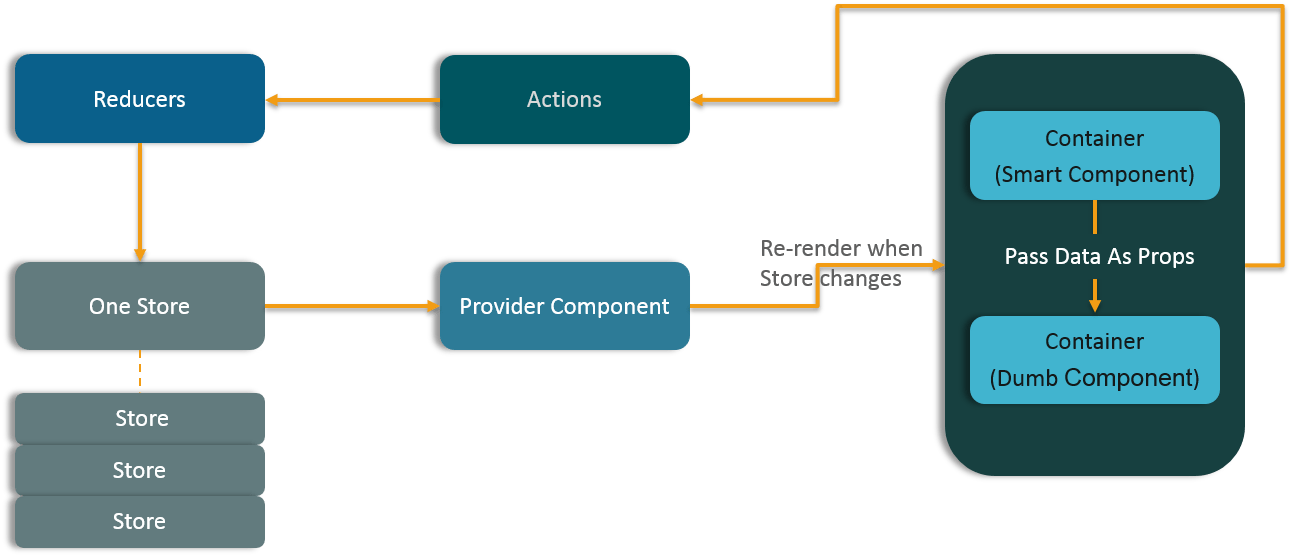
A store is a JavaScript object which can hold the application’s state and provide a few helper methods to access the state, dispatch actions and register listeners. The entire state/ object tree of an application is saved in a single store. As a result of this, Redux is very simple and predictable. We can pass middleware to the store to handle the processing of data as well as to keep a log of various actions that change the state of stores. All the actions return a new state via reducers.
21) How is Redux different from Flux?
| Flux | Redux |
|---|---|
| 1. The Store contains state and change logic | 1. Store and change logic are separate |
| 2. There are multiple stores | 2. There is only one store |
| 3. All the stores are disconnected and flat | 3. Single store with hierarchical reducers |
| 4. Has singleton dispatcher | 4. No concept of dispatcher |
| 5. React components subscribe to the store | 5. Container components utilize connect |
| 6. State is mutable | 6. State is immutable |
22) What are the advantages of Redux?
Advantages of Redux are listed below:
- Predictability of outcome – Since there is always one source of truth, i.e. the store, there is no confusion about how to sync the current state with actions and other parts of the application.
- Maintainability – The code becomes easier to maintain with a predictable outcome and strict structure.
- Server-side rendering – You just need to pass the store created on the server, to the client side. This is very useful for initial render and provides a better user experience as it optimizes the application performance.
- Developer tools – From actions to state changes, developers can track everything going on in the application in real time.
- Community and ecosystem – Redux has a huge community behind it which makes it even more captivating to use. A large community of talented individuals contribute to the betterment of the library and develop various applications with it.
- Ease of testing – Redux’s code is mostly functions which are small, pure and isolated. This makes the code testable and independent.
- Organization – Redux is precise about how code should be organized, this makes the code more consistent and easier when a team works with it.
React Router – React Interview Questions
23) What is React Router?
React Router is a powerful routing library built on top of React, which helps in adding new screens and flows to the application. This keeps the URL in sync with data that’s being displayed on the web page. It maintains a standardized structure and behavior and is used for developing single page web applications. React Router has a simple API.
24) Why is switch keyword used in React Router v4?
Although a <div> is used to encapsulate multiple routes inside the Router. The ‘switch’ keyword is used when you want to display only a single route to be rendered amongst the several defined routes. The <switch> tag when in use matches the typed URL with the defined routes in sequential order. When the first match is found, it renders the specified route. Thereby bypassing the remaining routes.
25) Why do we need a Router in React?
A Router is used to define multiple routes and when a user types a specific URL, if this URL matches the path of any ‘route’ defined inside the router, then the user is redirected to that particular route. So basically, we need to add a Router library to our app that allows creating multiple routes with each leading to us a unique view.
1
2
3
4
5
| <switch> <route exact path=’/’ component={Home}/> <route path=’/posts/:id’ component={Newpost}/> <route path=’/posts’ component={Post}/></switch> |
26) List down the advantages of React Router.
Few advantages are:
- Just like how React is based on components, in React Router v4, the API is ‘All About Components’. A Router can be visualized as a single root component (<BrowserRouter>) in which we enclose the specific child routes (<route>).
- No need to manually set History value: In React Router v4, all we need to do is wrap our routes within the <BrowserRouter> component.
- The packages are split: Three packages one each for Web, Native and Core. This supports the compact size of our application. It is easy to switch over based on a similar coding style.
27) How is React Router different from conventional routing?
| Topic | Conventional Routing | React Routing |
| PAGES INVOLVED | Each view corresponds to a new file | Only single HTML page is involved |
| URL CHANGES | A HTTP request is sent to a server and corresponding HTML page is received | Only the History attribute is changed |
| FEEL | User actually navigates across different pages for each view | User is duped thinking he is navigating across different pages |
References:-
https://blog.bitsrc.io/tagged/react
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/reactjs-lifecycle-components/
https://jscomplete.com/learn/1rd-reactful#initializing
Interview questions links
https://www.edureka.co/blog/interview-questions/react-interview-questions/
https://github.com/sudheerj/reactjs-interview-questions
https://medium.com/@vigowebs/frequently-asked-react-js-interview-questions-and-answers-36f3dd99f486
https://www.toptal.com/react/interview-questions
https://hackr.io/blog/react-interview-questions
https://mindmajix.com/reactjs-interview-questions
https://www.codementor.io/blog/5-essential-reactjs-interview-questions-du1084ym1
https://devhints.io/react
Code samples
https://jasonwatmore.com/post/2017/09/16/react-redux-user-registration-and-login-tutorial-example
https://stackblitz.com/edit/react-redux-registration-login-example?file=index.js
https://github.com/redgoose-dev/react-photo-layout-editor
Nice and good article.It was very interesting and meaningful.This is incredible,I feel really happy to have seen your webpage.I gained many unknown information, the way you have clearly explained is really fantastic.
ReplyDeleteFull Stack Training in Chennai | Certification | Online Training Course
Full Stack Training in Bangalore | Certification | Online Training Course
Full Stack Training in Hyderabad | Certification | Online Training Course
Full Stack Developer Training in Chennai | Mean Stack Developer Training in Chennai
Full Stack Training
Full Stack Online Training
Great Post. Keep Up with your good work.
ReplyDeleteReactjs classes in Pune